See also the articles "The Origins of the ‘European Social Model’" and "Organizing the International System" in the EHNE.
Definition
For decades, "Model Europe", understood as a continually growing and geographically expanding confederation of states, whose members display a high degree of social homogeneity and solidarity, and who have banned war as a means of resolving their differences, has been the object of a worldwide, and generally positive, discussion. The name "model" suggests the concept of a "role model", and indeed, Europe's exemplary character has brought forth a few attempts in other regions to create state confederations. Two examples of such efforts are the Andean Community (Comunidad Andina de Naciones, CAN) and the Mercado Común del Sur (Mercosur). However, these attempts either failed completely, or failed to develop beyond the stage of economic cooperation. The term "Model Europe" refers to a decision made against the background of nationalism, state rivalries, and the devastating conflicts of the 20th century, to create a federally structured organism of states. Under the banner of a policy of peace "Model Europe" guarantees economic prosperity, social justice, a supreme commitment to human and civil rights, and parliamentary democracy as the binding state form, along with a minimum consensus on common foreign and security policies. For this reason, during the division of the continent, the concept – the genesis of which will be discussed in detail below– did not include the entire continent but, initially, only the western part in which the first successful and permanent constructive attempts to realize the model were made. It would be interesting to explore the question of whether the concept was applied to the Europe of the Council of Europe or to the 1976 Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE). Generally, the term refers to the political constitution that emerged after 1989 when the East Central and South Eastern European states became free to join "Model Europe". Today the organization has become one of the most important global players, even if it has not been spared such negative catchwords as "disenchantment" with Europe ("Europamüdigkeit"), "Eurosclerosis" or "Eurocracy"; a state of affairs that can only be intimated here.
The Discussion of "Model Europe"
In essence, the notion of a "Model Europe" has been contemplated and discussed for centuries, even if under different names. Naturally, in the early stages it was a topic among intellectuals and public servants and not among the general population. However, it is also true that such thought and discussion found a remarkable echo. This discourse arose, and began to grow, at first slowly but then more rapidly, due to – perceived or de facto – external threats, or to threats occasioned by European inter-state relations. These latter threats to the variety and diversity of Europe came about through the occasional growth of European "super powers"; a development generally subsumed under the concept of "universal monarchy" in the pre-modern period. It is no coincidence that in the middle of the 15th century, at the beginning of the discourse on Europe, the Ottoman Empire was advancing toward the continent, a development symbolized by the fall of Constantinople in 1453. Pope Pius II (1405–1464) later made this event the basis for his appeal to the European powers to join in their hour of supreme danger to create an organisational structure that would endure. The Ottoman threat to, at least, parts of Europe was later used many times as a pretext for calling a European confederation of one kind or another – including "Holy Alliances"—into being. In pamphlet literature and journalism, we find this motive still alive in the 18th century, although by that time the Ottoman Empire had long lost the power to threaten even the middle of the continent.
Wars between European states themselves constituted a second structural element that advanced plans for a European federation that would go beyond coalitions made on a case-to-case basis. Whether during such wars or following them the discourse on Europe regularly intensified among intellectuals who called for the creation of structures to ban war from the life of European states forever: the heart of the concept of "Model Europe". This was true in regard to the Thirty Years War, the Napoleonic Wars, the Eastern and Western wars of the early 18th century (the Great Northern War, the War of Spanish Succession), and the world wars of the 20th century.
A third starting point for drawing up a blue print for "Model Europe" was the notion that with such a concept the framework of the participating states' internal politics could be brought into harmony. In the 19th century, this framework included freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, and limiting the power of the crown; in the 20th century, it included bringing the ethical aspects of economic life and the social question into accord. In this regard, authors, like Henri de Saint-Simon (1760–1825), to name just one important figure of the early 19th century, hoped for a permanent balance of standards. Today the European Union (EU) aspires to the same goal when, in the process of admitting new members, it requires that candidates for admission measure up to the standards of the "baskets" in their entirety. In other words, the "under developed" should profit from the accomplishments of the "pioneers".
Finally, a fourth motivating factor to think about a "Model Europe", under whatever name, but in the sense of close cooperation, was the challenge of competing models. Shortly after 1800, an intense discussion began concerning Model USA, from which it was believed that Europe could learn a great deal with regard to the organisation of a confederation of states and the economy. One of the first leaders in this effort was the economist and finance expert, active in Denmark, Conrad von Schmidt-Phiseldeck (1770–1832)[
![Richard Coudenhove-Kalergi (1894–1972) Schwarz-weiß Photographie, o. J. [vor oder 1936], unbekannter Photograph; Bildquelle: Coudenhove-Kalergi, Richard: Europa ohne Elend: Ausgewählte Reden von R. N. Coudehove-Kalergi, Wien 1936.](./illustrationen/europa-netzwerke-bilderordner/richard-coudenhove-kalergi-189420131972/@@images/image/thumb)
The various threads that must be differentiated in the discussion of Europe, and the long period of time which it took for the idea of "Model Europe" to mature, are factors that have led to various European models; sometimes Europe is thought of in a comprehensive way, at other times in a more restricted manner. The range is broad. On the one hand, there was the post-war notion of Europe – in the sense of the non-communist part of Europe – that at the end of the process of unification would be a single federal state. In contrast to this idea, that would severely limit the member states' sovereignty, there was the notion of a loose association of states joined together in a common representation of interests, for example in economic matters. The contemporary construction of the EU, still difficult to define in terms of international law, is located between these two notions; it is a federation of states that have delegated many sovereign rights to a common administration. This is the "Europe of the nations" evoked by Charles de Gaulle (1890–1970)[
The Characteristics of "Model Europe"
From a rather early date, the contours of "Model Europe" took shape due to the specific features of the continent, which is rather an extension of a larger continent (from which it can hardly be separated). From the beginning, it was clear that the elaborately structured continent would resist the growth of empire and favour the existence of a variety of communities. The absence of an all-inclusive empire provided Europe with aspects not found on other continents to the same extent: competition, rivalry, and a tense co-existence that often led to war. Europe came into being through this competition and these wars, and for long periods of its history, its signature was war. In addition to the Hundred Years War, the Eighty Years War, and the Thirty Years War, a number of centuries were marked by wars of dynastic rivalry. Against such a background, almost of itself, the question of whether wars between states constitute a law of nature, or whether the continent could eliminate them from its territory, gained in importance.
A second characteristic of Europe is freedom. In various degrees, freedom was native to the continent from the time the Ancient world ended. God was considered to be at the foundation of every form of rule, and government without the participation of the "subjects" was inconceivable. The forms of order in Europe ruled out the notion of an empire dominated by an autocrat who would govern without regard to his subjects' freedom. This was true for the Late Middle Ages' system of estates and their periodically convening assemblies, for the institution of municipal autonomy, for the freedom enjoyed by nobles below the rank of monarch, and for the system of justice that guaranteed a minimum of personal freedom. Even at the height of "Absolutism", and in France, the so-called motherland of "Absolutism", it was impossible to eliminate some forms of freedom. Nor in the early pre-modern era could the Tsar of Russia suppress certain of the nobles' regional rights.
Finally, freedom also meant the right to decide in matters of religion and the option to choose a non-conformist form of Christianity. Despite the fact that since the fifth century, following the fundamental decision in favour of Roman Catholic Christianity, large parts of the continent were unified religiously, it proved impossible to prevent groups from separating from the Church and its rites. Those who separated from Rome were branded "heretics" and thus stigmatised with the mark of Cain. Whether one considers the Cathar, the Waldensians, the Hussites, or the Anabaptists – Europeans were never willing to surrender the freedom to decide for themselves the nature of their relationship to transcendence. In the last instance, this consciousness produced what, in the 16th century, under the banner of "Reformation", led to the permanent division of Western Christianity. At the same time it must be emphasised, that with regard to the common foundation in the Holy Scriptures, the idea of the Trinity, and with regard to the faith in Christ's Second Coming, and other issues, the continent remained homogonous. Even the religious wars of the 16th century could not bury entirely the consciousness of the fact that Europeans shared the same spiritual and religious culture. The French "Politiques" at the end of the 16th century repeatedly emphasised this common religious culture.
Thus, it was hardly a coincidence that, "Model Europe" came into being at the end of a war that surpassed in destruction everything that had gone before. A number of elements had steadily nourished the idea of the need for the continent to grow together. Despite conducting many wars within a rather confined space, the rivalry between European states never permitted the founding of an empire. The freedom of the individual or of social groups, right up to the 19th century, banished the notion of a "strong" state that could control everything down to the local level, into the realm of dreams. This relative homogeneity in religious affairs nevertheless permitted states to "take their own path", such as the British did in the 16th century. Thus, there were moments in which Europe appeared relatively unified. Long before "Model Europe" would become reality, it was to such moments that intellectuals and civil servants recurred in their thoughts on a future for Europe in "peace and freedom".
The list of men – there were few women – who in pamphlets, journalism, and literature were concerned with the physiognomy of a Europe thus understood, reads like a Who's Who in European intellectual and political history. There are literary figures such as Novalis (Friedrich Freiherr von Hardenberg, 1772–1801)[






![Gustav Stresemann (1878–1929) IMG Schwarz-weiß Photographie, o. J. [vor oder 1929]; Bildquelle: Library of Congress, George Grantham Bain Collection, DIGITAL ID: (digital file from original neg.) ggbain 32589 http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.pnp/ggbain.32589.](./illustrationen/briand-plan/gustav-stresemann-187820131929-img/@@images/image/thumb)
![Winston Churchill (1874–1965) IMG Winston Churchill (1874–1965), Schwarz-Weiß-Photographie, 1943, unbekannter Photograph; Bildquelle: © Franklin D. Roosevelt Presidential Library and Museum [http://docs.fdrlibrary.marist.edu/wwphotos.html], Photos of World War II, http://docs.fdrlibrary.marist.edu/images/photodb/23-0201a.gif.](./illustrationen/modell-europa-bilderordner/winston-churchill-187420131965-img/@@images/image/thumb)
Europe as a Community of Values
It was clear to these men that, arising from the particular political situation at any given time, there were rational grounds to support the call for a federally based European unification. They were also aware that additional elements would be needed in order to breathe life into such a construction. Even if they did not often say so, they realized that the future of Europe would require that it be more than a community of common experiences; it would also have to be a community of values. We have spoken of these values above, and it is no coincidence that the beginning of the process of Europeanization took place with the founding of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR)3 at the end of the Second World War, that remains in force to this day. No other continent has a comparable document.
Naturally, throughout the world, all states have been called upon to observe the 1948 United Nation's Universal Declaration of Human Rights4, but nowhere else have these rights become binding. This document is at the heart of European identity. It was enacted by the Council of Europe in 1950 against the background of the Hague Congress of May 1948


The fundamental consensus on values, which for a long time has constituted the specific nature of the continent, is one reason why attempts to copy or adopt the model elsewhere have failed. Contiguity or merely partial common interests – for example, collective security or trade – are not sufficiently strong grounds for keeping a political organization alive over time. A clear example of this problem is the so-called Andean Community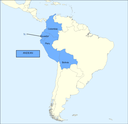
Competing Models
Naturally in the course of modern history, and primarily in the course of recent history, not only were plans for a "Model Europe" put forward that approximated the current one, but also plans that differed from it widely. Napoleon's Europe, with its strict orientation to Paris, was incompatible with the models that had been discussed up to that time which, without exception, had called for a federalist foundation that respected the sovereignty of individual communities. The "New Europe" of Adolf Hitler (1889–1945) also departed from the pre-Napoleon models, which is not to say that there is a direct line from Napoleon's notion to that of Hitler. One of the great perversions of the politicized historical speculation of this latter period was the National Socialist ideologues' continual evocation of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. With the beginning of the war against the Soviet Union in 1941, they identified the creation of a "New Europe" with an anti-Bolshevik crusade, which became an essential element of Nazi propaganda. National Socialist propaganda made the battle of Stalingrad into a symbol of "Fortress Europe's" defence of the West. In March 1943, Joseph Goebbels (1897–1945) and Joachim von Ribbentrop (1893–1946) expressed their views on the physiognomy of the "New Europe". Ribbentrop was more circumspect, but both men were in basic agreement on the model they had in mind, which Goebbels had already outlined in a talk to Czech intellectuals in the autumn of 1940:
Dann wird unser großes volksstarkes Reich neben Italien praktisch die Führung Europas übernehmen. Daran ist gar nichts mehr zu drehen und zu deuteln. Das heißt also für Sie: Sie sind jetzt schon ein Glied eines großen Reiches, das sich eben anschickt, Europa eine neue Ordnung zu geben. Es will die Schranken, die die europäischen Völker noch voneinander trennen, niederreißen und ihnen den Weg zueinander ebnen.6
As early as 1941, Ribbentrop spoke of "the already existing and continually growing moral unity of Europe in the New Order that our great leaders have announced and which they have prepared for the future of the civilised nations. This is the profound meaning of the war against Bolshevism. It is the sign of Europe's spiritual re-birth."7 Numerous propaganda meetings and posters bombarded the occupied states, for example France, with this message: "L'Europe unie contre le bolchevisme" ["Europe united against Bolshevism"]
At the same time, and at a different place, men and women thought about a post-war order that would take up traditions that differed dramatically from National Socialist fantasies. Even if the men and women of the German resistance, the exiled brothers Heinrich and Thomas Mann, or Winston Churchill, differed in their view of the goals, and emphasised very different points, they were nevertheless of one mind in their rejection of every solution that foresaw a centralized Europe. Their shared maxim was to do everything possible to prevent totalitarianism from again having a chance to create a European central state, and to do everything possible to banish war from European territory. A short section of a typescript from the autumn of 1943, written by the former mayor of Leipzig, Carl Friedrich Goerdeler (1884–1945)[
"Model Europe" in the Historical Sciences
Last, but not least, "Model Europe" – avant la lettre – had an enduring influence on historical science. While it is true that the orientation of most national historical cultures in the 19th and in the first third of the 20th century, were unambiguously nationalist, if not indeed chauvinist, still, from the 18th century onward there were repeated scholarly attempts to discover the "essence" and particularities of Europe and present them in scientific works. Even if Leopold von Ranke (1795–1886) never wrote a "History of Europe", his historical reflection was oriented to Europe in its entirety. His view took in both Serbia and the Papacy, both France and Venice. The lectures published under the title of Über die Epochen der neueren Geschichte9 emphatically demonstrate this European dimension. Nevertheless, one need not point first to this grand master of historical science to find such a European horizon. There are a number of other important representatives of this perspective. The biographer of August Ludwig von Schlözer (1735–1809) speaks of the inner connectedness of European experience as being of fundamental importance to Schlözer. "For him, Europe was not a system, but an aggregate of states with varying forms of rule, in which dynastic, diplomatic, religious, ethical and economic relationships and interfaces existed".10 In this regard, one can also point to the diverse studies of Arnold Herrmann Ludwig Heeren (1760–1842) on the structure of modern European systems of power.11 One can also point to Friedrich Ludwig Georg von Raumer (1781–1873), even if his eight volume Geschichte Europas seit dem Ende des fünfzehnten Jahrhunderts (1832–1850)
Popular Movements
However, historians did not make the idea of Europe and the concept of "Model Europe" popular. This task was accomplished by the great movements, beginning in the interwar period, which reached large numbers of people in the various European states. Among these was the Paneuropa Movement of Coudenhove-Kalergi during the interwar period, and the Europa-Union that started in Switzerland in the late 1940s and exists to this day. If the mark of these movements was that they were above parties, other movements did maintain ties to political causes. Among these were the pacifist movements that organized under the banner of communism, and whose world congresses evoked a Europe quite different from the one that began to form in 1957. Some of the pacifist movements – including some during the interwar years – oscillated between pacifism and Europeanism, modifying their activities according to the emphasis that they pursued at any particular time. If the "Model Europe" of the recent past again and again reflected on its spiritual foundation and made it a theme of its discourse, this was in large part in reaction to the Soviet dominated system of the Warsaw Pact, and in response to an organization that at least verbally claimed to represent a number of European values. In 1989/1990, this challenge ceased to exist and the history of European integration since then has often demonstrated a considerable gap between verbal commitment to the ECHR and actual practice.
To this day, the EU has had considerable difficulty with symbolical acts and ceremonies. It has been very difficult for the EU to establish a publically successful forum for "Model Europe". The awarding of the Charlemagne prize of Aachen since 1950 has remained a local initiative for acknowledging those who have done great service in the interest of Europe, and has not been elevated to the rank of an official act sponsored by the European Parliament. The project of establishing a central museum for "Model Europe" has been under discussion for decades, but up to now with no tangible results. Large exhibitions like the one in Cologne in 1979 in the run-up to the first European elections18 or the 2003 exhibition in Berlin19 attract those interested in culture and politics, but cannot speak to all the various groups of the population in the same way. In addition, many programmes in support of Europe are only partially suited to attracting great numbers of people and to strengthening their European identity. If it were not for the Euro, the European flag,

The Fascination of "Model Europe"
However, none of the above has diminished the fascination that "Model Europe" has for external observers. Here for the first time in history sovereign states have made an attempt, and found a way on a voluntary basis while observing a binding stock of values, to create an enduring community in which war as a means of realizing interests has been banned forever. In the meantime, this community has grown to embrace almost thirty states, extending from the North Cape to Cyprus and from Algarve to the Black Sea. "Model Europe" is a success story with small fractures. Where others have tried to imitate it, they have not been successful. It is idle to reflect on why the model functions in Europe but not elsewhere. However it appears that one important factor that distinguishes "Model Europe" from attempts to imitate it, for example that of the Andes states, is that European states share deeper roots based on a community of experience and– in varying degrees – share a number of common values, that have developed over the centuries. Indeed this is what Jean Monnet (1888–1979)[
[Inzwischen] haben über die Institutionen hinaus – und als tiefes Bedürfnis der Völker – die europäische Idee und der Geist gemeinschaftlicher Solidarität Wurzeln geschlagen. Diese Idee "Europa" wird allen die gemeinsamen Grundlagen unserer Zivilisation vor Augen führen...20