From the Beginnings until the 15th Century
The beginnings of the immigration of Jews from France and Germany (the so-called Ashkenazim) to Eastern Europe are largely obscure. Clearly, up into the mid-13th century, there were only small groups of Jews in Eastern Europe. They were in contact with the Ashkenazi centres and probably also originated from there. However, these family groups do not seem to have left any traces. Bernard Weinryb quotes an exchange of letters from the 1210s in which the Rabbi Judah ben Samuel ("the Pious") (ca. 1150–1217) of Regensburg informed Rabbi Eliezer ben Yitzhaq of Prague that Jews without religious education lived in the territories of what is now Poland and Russia: without the support of their fellow Jews from Central Europe, they would remain without a knowledge of the Torah and Halakha and without organised religious services.1
The question of the early Jewish settlement in Eastern Europe and its cultural achievements is currently arousing great interest, above all among Russian Slavicists:2 some have sought to postulate a Jewish centre in Kievan Rus' during the late Middle Ages which supposedly had a leading role in the composition of certain Russian Church Slavonic documents (for example the Old Church Slavonic translations of the Book of Esther and the Book of Josephus).3 The goal of this ideologically motivated hypothesis (which has since been disproved)4 is to demonstrate the independence of early Russian literature from its South Slavic models.5
In contrast, Weinryb describes the Jewish immigration to Eastern Europe in the early modern period thus: "The thirteenth and particularly the fourteenth centuries should be regarded as the time of real Jewish settlement in Poland; in the twelfth century only a few individuals or small groups may have existed there."6
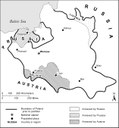
The real immigration to Eastern Europe7 began when the legal conditions for Jews improved considerably thanks to the charters issued by the Polish Duke Bolesław V (1221‒1279) in 1264 and by King Kasimir the Great (1310‒1370) in 1334.8 In Lithuania, the Grand Duke Vytautas the Great (ca. 1350‒1430) created important privileges for the Jews of Brest-Litovsk and Trakai in 1388;9 and as a result an important Karaite community settled in Lithuania.10
These rulers hoped that Jewish immigrants, encouraged by such edicts, would be qualified labourers who would help with the reclamation of land and the development of trade and thereby benefit the royal exchequer; in return, the Jews received privileges that, for the late Middle Ages, were exceptionally generous: the royal protection, through which the Jews – in a sense – belonged to the royal treasury and thus occupied a special position in the population, and the right to self-administration in ritual and judicial matters through the local organisation of the qahal (Jewish community), which collected taxes and was a legal link to the king.11 In addition, there was the freedom of movement, although this was restricted by the right of many free cities to refuse Jews residence (the so-called privilegium de non tolerandis Judaeis) because the local merchant guilds feared competition. As early as the 15th century, differences had emerged within the Jewish community in Poland between those living in the city and those from the countryside. Like their Christian neighbours, urban Jews lived in their own quarters, for example in Krakow's Judengasse (Jew Lane).12
The 16th Century
In the 16th century the Polish kingdom underwent two major changes. Firstly, in 1569, it became a multi-religious, multi-ethnic state as a result of its territorial expansion to the east through the union with Lithuania. Besides the Catholic Poles and Lithuanians, there were now Protestant subjects, for example in the Hanseatic cities, and a strata of Ukrainian Orthodox peasants in the eastern regions. Secondly, these new territories (above all those in today's Ukraine, including Podolia) were incorporated into the political structures of Poland-Lithuania. This was achieved as a result of the policy of colonisation pursued by the nobility (szlachta), who above all sought to enlist Jewish tax farmers (the so-called system of faktorstwo). These tax farmers also had the right to distil and sell alcohol (propinacja).
At about the same time, the crown, which had been relatively week since the late Middle Ages, was largely stripped of its power as the key functions of legislation and financial policy were transferred to the parliament of nobles, the Sejm.13 Weinryb talks of a "fragmentation of power":14 the individual members of the szlachta took on the nominal sovereignty and the rights and duties of the king so that in their own territory they presided over a "state within a state"; these practically autonomous areas were only loosely held together by the Sejm in matters of common importance. Given that the nobles in the Sejm had the right to veto royal decrees (even during war), the Rzeczpospolita (to use the self-designation of Poland-Lithuania, a borrowing from the Latin res publica) was no longer capable of functioning. The fateful repercussions of this concentration on private self-interest and the resulting deadlock became evident in the second half of the 18th century when the Rzeczpospolita was destroyed and Poland partitioned.
In the 16th century, the landed nobility, who were primarily involved in the colonisation of the east, took over the royal privileges for the Jews:15 tax farming, which had been transferred to the Jews in Poland by King Sigismund I (1467‒1548),16 was administered from now on by the nobles on their own territory.
In the areas ruled by the members of the szlachta, the shtetl now emerged – Jewish settlements in Eastern Europe with their distinctive architecture geared towards Jewish religious law (Halakha). For example, in several regions they possessed the characteristic winter gardens (kusha) that could be easily used during the Feast of Tabernacles to construct a tabernacle. In addition, because Jews were only allowed to walk a short distance on the Sabbath (the Sabbath day's walk), synagogues were built close to residential housing.17
Jews in the countryside were accorded the role of intermediaries between the nobles and the Ukrainian and Polish peasants: within the aristocratic fiefdoms, they were responsible not only for tax collection, but also received the alcohol monopoly granted by the king.
As a result, the lion's share of the Rzeczpospolita's income came from Jewish leaseholders who were accountable to the nobles. One important reason for this was the self-contained flow of money: the nobles got back a large portion of the money they paid as wages to the peasants from the sale of alcohol because Jewish leaseholders had to hand over part of their profits to the nobles.18 Inherent to this role as an intermediary (i.e. the Jews' socio-political link to the landlords and their representation of the nobility vis-à-vis the peasants) was the danger that Jews in the countryside would be the target of social dissatisfaction and serve as a scapegoat due to their trade in alcohol, which was rejected by the Catholic clergy on moral grounds.19 In this anti-Jewish climate, which was particularly encouraged by the Catholic church in Poland, the number of blood libel trials

In 1598, for instance, a child's body was found near Lublin. This triggered an avalanche of blood libel trials,22 which continued in batches for the rest of the following century. In connection with this, the sources indicate increased Jewish migration from the central Polish region to the new territories in the east. There they received the relative protection of the landlords, who also possessed juridical authority.
The Jews' self-administration also underwent a change in the 16th century: the Jewish communities were increasingly led by a plutocratic ruling class, and tensions between the interests of the rich and poor developed that were to exist until the end of Poland-Lithuania.23 This discrepancy was exacerbated by the decline of long-distance trade to the benefit of a large number of travelling merchants and other small traders.24 On account of the constant high tax debts to the crown, the communities had to take up large loans from local monasteries, and the interest charged by the latter increased the impoverishment of the Jews. In order to represent Jewish interests in Poland, the Jewish communities throughout the country banded together to create the so-called Council (Wa'ad) of Four Lands in 1582; Lithuania received its own umbrella organisation.25
At this time, the office of a Jewish representative (the shtadlan) at sittings of the Sejm was introduced. He could follow political decisions and was meant to prevent the passing of laws that could have a negative impact on the community. To do this, the shtadlan was present at the individual meetings of the Sejm and tried – sometimes using bribery – to influence decision making or at least convince a noble to use his veto.
The 17th Century
The migratory movement from Central Europe begun in the late Middle Ages continued in the 17th century. The migration within Poland-Lithuania towards the east of the country also persisted. In addition, many Jews moved from Austria and Bohemia (parts of the Habsburg Monarchy) to Hungary.
With hindsight, one can talk of a century of decisive change for the Jews of Central and Eastern Europe because these three migratory movements created the distribution of population that would largely remain in place up into the 20th century. The communities stabilised and East European Jewry ensured its leading role within the diaspora; Vilnius in Lithuania (Polish: Wilno; Yiddish: Wilne) became a renowned centre for the study of the Talmud, whose writings were read even in far away Central Europe. The Jewish opposition to the Orthodox monopoly on the leadership of the qahal that would later develop was not yet evident in the 17th century.26 Nevertheless, one can still see a certain degree of alienation of officials from the daily life of the population as a result of a legalism maintained by some scholars, which was connected to emphatic sermons on repentance and punishment.
The political situation in Poland-Lithuania became critical in the first half of the 17th century. Whereas the Thirty Years' War in Germany came to an end in 1648, this year saw an escalation of violence in the eastern part of Poland-Lithuania. The relationship between the religious and social groups on the szlachta estates had always been tense; now the conflict exploded between the Polish-Catholic nobles, the Jewish leaseholders and the Ukrainian-Orthodox peasants in a Cossack rising led by their Hetman Bohdan Chmielnicki (1595‒1657).
The different religious faiths of those involved gave the social conflict an additional edge. Under their new leader, the Ukrainian Cossack rebels, who had originally been a self-organised militia formed to defend the Crimea against the raids of the Tatar Khanate, turned against the feudal system in the new territories of Poland-Lithuania and against the dominant position of the Polish landed aristocracy and the Jewish leaseholders, who in their eyes were the representatives of the feudal system. The rising, which between 1648 and 1656 caused massive devastation, reached a first climax as early as April and June 1648 when the Cossacks destroyed many Polish villages and cities. Many members of the non-Ukrainian or non-Orthodox population were barbarically murdered; others were forced to convert to Orthodoxy. In addition, many Jews in this region were enslaved by local traders and sent as part of the slave trade to the Ottoman Empire or at least to the Ottoman territories, which at this time included Podolia
Because the province of Podolia fell to the Sublime Porte as a result of the Polish-Ottoman Wars of 1672‒1699, further connections to the Ottoman Empire developed. This short intermission was not only important because it simplified the migration of Jews into the heartland of the Ottoman empire (for example, in this period the number of immigrants to Palestine increased), but also because Podolia acted as a cultural bridgehead across which the Messianic tension of the Sephardic Jews in the Ottoman Empire could be transferred to Eastern Europe. Podolia was especially important for the Messianic movement of Sabbateanism, although its extent has not yet been thoroughly investigated. The threatening and traumatising news of the situation of the Jews in Eastern Europe certainly helped lend plausibility to the teachings of Shabtai Zvi (1626‒1676)[
The Sabbatean movement apparently emerged from a complex interaction of Messianic trends among the former Marranos (Sephardim who had converted to Christianity and returned to Judaism in the Ottoman Empire) and the Kabbalic impulses of the Jewish mystic Isaak Luria (1534‒1572) – an interaction which had a powerful effect under the impact of the catastrophic events of 1648. Sabbatean ideas also came to Poland-Lithuania via Podolia.28 At any rate, the Kabbalah, on which Sabbateanism drew, offered the Sephardim (and a small number of Ashkenazim) ways of interpreting the suffering inflicted upon them by the Cossacks.
The 18th Century (until the Partitions of Poland)
The trends of the 17th century continued into the 18th century. The debts of the Jewish communities acquired massive proportions; the tax debt of Jews in Poland-Lithuania came to roughly three million złoty and accounted for a monstrously big portion of the communal budget.29 The communities were barely able to cover their other expenses, for example the maintenance of the Jewish school system (boys between five and twelve years old had to attend the Jewish primary school, the Cheder), the payment of rabbis and other communal officials,30 and the upkeep of charitable institutions; the corruption of the local authorities and the associated bribes for state organs at the local and supraregional levels also had to be taken into account. The preference given to wealthy community members in the setting of tax debt exacerbated the impoverishment of the other Jews. The solution was to introduce or increase communal taxes: thus, when a noble accepted a bid from a prospective Jewish leaseholder, the leaseholder had to pay a license tax to the community; in addition, a so-called basket tax on kosher meat was introduced. In order to regulate migration, a tax on settlement was put in place. However, even these measures were not enough to put the communities' finances in order after Poland-Lithuania introduced a tax reform in 1764 that increased the financial difficulties of the Jewish communities.
The centralisation evident in the 16th and, to a certain extent, the 17th centuries, which guaranteed Jewish representation in the form of the Council of Four Lands and the Lithuanian Wa'ad, was reversed in the 18th century. The loss of power by both synods was accompanied by a further regionalisation and the consolidation of local communities.31
Despite the disastrous consequences of the Cossack rising for the Jews, the Jewish population continued to increase significantly in the 18th century. During the Polish-Lithuanian tax reform in 1764, investigations revealed that roughly seven percent of the Rzeczpospolita's population were Jews,32 who can be broken down first into urban and rural residents and then by income group. On the szlachta leaseholds, Jewish servants and indeed many sub-lessees lived in addition to the wealthy leaseholders. The cities contained a small upper class of merchants, who were even admitted to the guilds and the municipal administration in the Russian Empire after the partitions; on the other hand, the majority of Jews were small traders or practised specific crafts (above all, as cobblers, tailors33 and tanners).
Although there had already been blood libel trials against Jews in earlier centuries, their number now increased considerably. One must take into account the fact that the intellectual heritage of Humanism and the Renaissance, as well as Absolutism and its modernising implications, had not yet altered the feudal system of Poland-Lithuania. This situation, which was underpinned by poverty, a lack of education and a superstitious worldview, repeatedly produced Jewish blood libel trials; one can assume at least 20 trials in the first 60 years of the century.34 The affliction become so great that in 1763 Jewish emissaries complained to Pope Clement XIII (1693–1769) in Rome and called upon him to intervene in their homeland. Pressure from the Pope and King August III (1696‒1763) curtailed the number of trials, which had been fomented by the local clergy, who shared the population's worldview.35
Among the Jews of Eastern Europe, one also finds a worldview shaped by such existential angst. There prevailed a perception of living in a hostile world full of demons, against whom one tried to guard oneself through various magical practices and amulets. Many so-called Ba'alei Shem (masters of the name [of God]) worked as healers and magicians with apotropaic powers. Using a combination of common magical rituals and elements of the 16th-century Kabbalah, they offered their services to the population. The founder of Hasidism, Israel ben Eliezer Ba'al Shem Tov (acronym: Besht) (ca. 1700–1760) also acted as such a miracle worker.
A similar crisis to that of the Cossack pogroms in the 17th century arose in 1768 during the haidamaky rising of Ukrainian peasants in the east of the country. The intersmediary position of the Jewish leaseholders in the Polish feudal system again led to Jews being used as a blank screen onto which social tensions were projected and the position of the Jewish communities became increasingly precarious.
In 1727 the Tsarina Catherine I (1684‒1727) expelled Russia's few Jews.36 Not until the Partitions of Poland (1772, 1793 and 1795),